Caching Strategy and Eviction Policies
Caching Strategy
대용량 아키텍처에서 성능(처리량)을 높이기 위해 적절한 Cache Strategy 와 함께 Cache Layer 를 도입하는 것은 효과가 좋다.
Cache Aside also known as Lazy Loading
Cache Aside: the application code is responsible for both retrieving and storing data in the cache.
Cache Miss 가 발생하면 데이터베이스를 쿼리하여 데이터를 읽고 클라이언트에 반환한 다음 데이터를 캐시에 저장해야 하는 추가 작업이 필요하다.
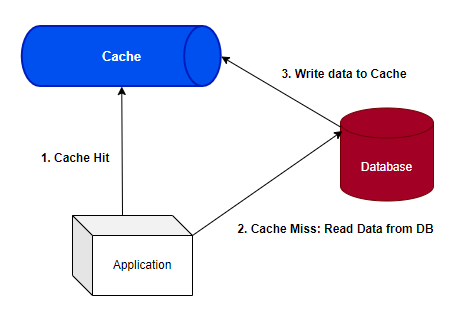
When cache-aside is used, the most common write strategy is to write data to the database directly. When this happens, cache may become inconsistent with the database. To deal with this, developers generally use time to live (TTL) and continue serving stale data until TTL expires. If data freshness must be guaranteed, developers either invalidate the cache entry or use an appropriate write strategy, as we’ll explore later.
장점으로는 캐시 클러스터가 다운되더라도 데이터베이스로 데이터를 조회하기 때문에 계속 작동이 가능하다. 또한 캐시 데이터 모델과 데이터베이스의 데이터 모델이 다를 수 있다.
EhCache 같은 것을 사용할 때 TTL 을 설정할 수 있다. (보통 XML 로 설정하는 것으로 알고 있음)
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = ["myCache"])
class MyService {
@Cacheable(key = "#id", unless = "#result == null", cacheManager = "myCacheManager")
fun getData(id: Long): String? {
// implementation to retrieve data from data source
}
@Cacheable(key = "#id", unless = "#result == null", cacheManager = "myCacheManager")
fun getDataWithTTL(id: Long): String? {
// implementation to retrieve data from data source
}
@Cacheable(key = "#id", unless = "#result == null", cacheManager = "myCacheManager")
fun getDataWithDynamicTTL(id: Long, ttlInSeconds: Long): String? {
// implementation to retrieve data from data source
}
}
// CacheConfig to set TTL for caching
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
class CacheConfig {
@Bean
fun cacheManager(): CacheManager {
val cacheBuilder = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // Set TTL to 60 seconds
return GuavaCacheManager().apply {
setCacheBuilder(cacheBuilder)
}
}
}
Read Through
Read Through 는 Cache Aside 와 반대로 원본 데이터를 읽어와 저장하는 책임이 Cache 에게 있다.
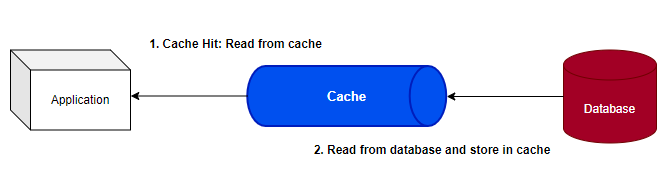
처음에는 캐시가 없기 때문에 Cache Miss 가 발생한다. 따라서 뉴스 기사 등 대량의 트래픽을 처리해야 하는경우 Batch 같은 Job 을 통해 cache warm-up 을 하여 캐시를 미리 로드해 놓고 처리할 수 있다.
캐시 배제(Cache Aside)와 달리 Read-Through 캐시의 데이터 모델은 데이터베이스의 데이터 모델과 다를 수 없다.
Write Through
Write-through(연속 기입) caching is a caching strategy where data is stored in the cache and the original data source simultaneously. When the application writes data, it writes to the cache first, and then to the original data source. This ensures that the cache is always up-to-date and reduces the risk of stale data. However, this approach can have high write latency due to the additional write to the original data source.

- The application writes the data directly to the cache.
- The cache updates the data in the main database. When the write is complete, both the cache and the database have the same value and the cache always remains consistent.
Write Back
Write-back caching is a caching strategy where data is written to the cache first, and then asynchronously written to the original data source at a later time. This can improve write performance, as the application only needs to write to the cache and the cache handles the write to the original data source. However, this approach can have higher read latency, as data in the cache may not always be up-to-date with the original data source.

후기입 캐시(write back cache)는 쓰기 성능을 향상시키고 쓰기 작업이 많은 워크로드에 적합하다. 쓰기 작업은 시간이 오래 걸리므로 Cache 에 모아 두었다가 Batch 같은 Job 으로 한꺼번에 처리하는 것이 효율적이다.
Most relational databases storage engines (i.e. InnoDB) have write-back cache enabled by default in their internals. Queries are first written to memory and eventually flushed to the disk.
Cache Eviction Policies
캐시 제거를 위한 정책도 필요하다.
- Least Recently Used:최근 가장 적게 사용된 캐시를 제거하는 것이다. 즉, 가장 오래 전에 마지막으로 사용된 값을 제거한다. 가장 많이 사용되는 전략 중 하나이다.
- Least Frequently Used: 가장 적게 사용된 캐시를 제거하는 것이다. Counter 가 필요하다.
- Most Recently Used: 가장 최근에 사용된 캐시를 제거하는 것이다.
- Most Frequently Used: 가장 자주 사용되는 캐시를 제거하는 것이다. Counter 가 필요하다.