Cascade
Referential Integrity and Cascade
Referential Integrity
Referential integrity is the logical dependency of a foreign key on a primary key. The integrity of a row that contains a foreign key depends on the integrity of the row that it references—the row that contains the matching primary key.
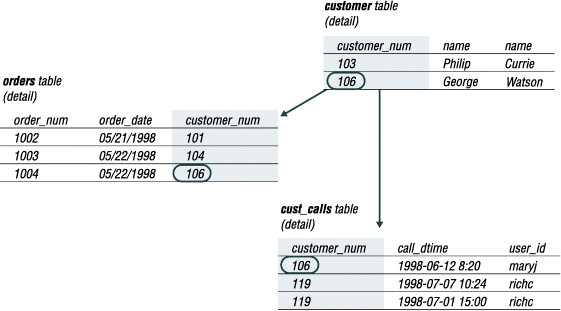
By default, the database server does not allow you to violate referential integrity and gives you an error message if you attempt to delete rows from the parent table before you delete rows from the child table.
ON UPDATE CASCADE
PK 테이블의 PK 값이 바뀔 때(1 to 2) FK 테이블에 있는 FK 의 값(1 to 2)도 같이 변경된다.
ON DELETE CASCADE
To maintain referential integrity when you delete rows from a primary key for a table, use the ON DELETE CASCADE option in the REFERENCES clause of the CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements. This option allows you to delete a row from a parent table and its corresponding rows in matching child tables with a single delete command.
ON DELETE SET NULL
PK 테이블의 레코드가 삭제될 때, FK 테이블에서는 레코드가 같이 삭제 되는 것이 아니라 FK 가 null 로 변경된다.
Cascade
JPA 에서도 연관 관계를 맺을 때 Cascade Option 을 사용할 수 있다.
CascadeType.ALL
CascadeType.ALL propagates all operations — including Hibernate-specific ones — from a parent to a child entity.
- Same as CascadeType.PERSIST + CascadeType.REMOVE
- CascadeType.ALL 옵션은 부모가 자식의 전체 생명 주기를 관리하겠다는 의미
CascadeType.PERSIST
CascadeType.PERSIST propagates the persist operation from a parent to a child entity.
CascadeType.MERGE
CascadeType.MERGE propagates the merge operation from a parent to a child entity.
CascadeType.REMOVE
CascadeType.REMOVE propagates the remove operation from parent to child entity. Similar to JPA's CascadeType.REMOVE, we have CascadeType.DELETE, which is specific to Hibernate.
CascadeType.REMOVE 는 부모 엔티티가 삭제되면 자식 엔티티도 삭제된다. 즉, 부모가 자식의 삭제 생명 주기를 관리한다. 만약 CascadeType.PERSIST 도 함께 사용하면, 부모가 자식의 전체 생명 주기를 관리하게 된다.
@Test
public void whenParentRemovedThenChildRemoved() {
int personId;
Person person = buildPerson("devender");
Address address = buildAddress(person);
person.setAddresses(Arrays.asList(address));
session.persist(person);
session.flush();
personId = person.getId();
session.clear();
Person savedPersonEntity = session.find(Person.class, personId);
session.remove(savedPersonEntity);
session.flush();
}
부모가 삭제되면 자식도 아래처럼 Hard Delete 가 발생한다.
Hibernate: delete from Address where id=?
Hibernate: delete from Person where id=?
반면, 부모 엔티티(Team)에서 자식 엔티티(Member)를 제거하는 경우에는 delete 쿼리가 나가지 않는다. CascadeType.REMOVE 옵션은 부모와 자식의 관계가 끊어졌다고 해서 자식을 삭제하지 않는다.
연관관계를 끊고 자식을 삭제하려면 아래 처럼 코드를 작성해야 한다.
parent.getSubList().remove(sub);
em.remove(sub); // em.remove 생략하려면 orphanRemoval = true 필요
em.flush();
CascadeType.DETACH
When we use CascadeType.DETACH, the child entity will also get removed from the persistent context.
CascadeType.LOCK
Unintuitively, CascadeType.LOCK reattaches the entity and its associated child entity with the persistent context again.
@Test
public void whenDetachedAndLockedThenBothReattached() {
Person person = buildPerson("devender");
Address address = buildAddress(person);
person.setAddresses(Arrays.asList(address));
session.persist(person);
session.flush();
assertThat(session.contains(person)).isTrue();
assertThat(session.contains(address)).isTrue();
session.detach(person);
assertThat(session.contains(person)).isFalse();
assertThat(session.contains(address)).isFalse();
session.unwrap(Session.class)
.buildLockRequest(new LockOptions(LockMode.NONE))
.lock(person);
assertThat(session.contains(person)).isTrue();
assertThat(session.contains(address)).isTrue();
}
CascadeType.REFRESH
Refresh operations reread the value of a given instance from the database. When we use this operation with Cascade Type REFRESH, the child entity also gets reloaded from the database whenever the parent entity is refreshed.
@Test
public void whenParentRefreshedThenChildRefreshed() {
Person person = buildPerson("devender");
Address address = buildAddress(person);
person.setAddresses(Arrays.asList(address));
session.persist(person);
session.flush();
person.setName("Devender Kumar");
address.setHouseNumber(24);
session.refresh(person);
assertThat(person.getName()).isEqualTo("devender");
assertThat(address.getHouseNumber()).isEqualTo(23);
}
CascadeType.REPLICATE
The replicate operation is used when we have more than one data source and we want the data in sync. With CascadeType.REPLICATE, a sync operation also propagates to child entities whenever performed on the parent entity.
@Test
public void whenParentReplicatedThenChildReplicated() {
Person person = buildPerson("devender");
person.setId(2);
Address address = buildAddress(person);
address.setId(2);
person.setAddresses(Arrays.asList(address));
session.unwrap(Session.class).replicate(person, ReplicationMode.OVERWRITE);
session.flush();
assertThat(person.getId()).isEqualTo(2);
assertThat(address.getId()).isEqualTo(2);
}
CascadeType.SAVE_UPDATE
CascadeType.SAVE_UPDATE propagates the same operation to the associated child entity. It's useful when we use Hibernate-specific operations like save, update and saveOrUpdate.
@Test
public void whenParentSavedThenChildSaved() {
Person person = buildPerson("devender");
Address address = buildAddress(person);
person.setAddresses(Arrays.asList(address));
session.saveOrUpdate(person);
session.flush();
}
OrphanRemoval
OrphanRemoval 은 Default 가 false 이다. 옵션을 true 로 설정하고 CascadeType.PERSIST 옵션을 같이 사용하면 부모가 자식의 전체 생명 주기를 관리하게 된다. CascadeType.PERSIST + CascadeType.REMOVE 조합과 다른 점은 부모 엔티티에서 자식 엔티티의 관계를 제거하면 자식은 고아(Orphan) 취급 되어 Hard Delete 로 제거된다.
Warning
CascadeType.PERSIST + CascadeType.REMOVE 와 CascadeType.PERSIST + orphanRemoval = true 두 케이스 모두, 자식 엔티티에 딱 하나의 부모 엔티티만 연관되어 있는 경우에만 사용해야 한다. 즉, 자식 엔티티의 참조가 하나의 부모를 대상으로만 해야 한다.
- 사용 기준
- Member(자식) 를 Team(부모) 도 알고 Partner(부모) 도 알고 있다면 두 옵션의 사용을 조심해야 한다.
- Entity 가 Aggregate Root 인 경우에만 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- e.g Order - OrderItem 의 관계에서 Order 쪽에 cascade 설정
- Order - Delivery 같이 관계가 애매한 경우에는 사용하지 않는 것이 좋다. Delivery 는 Order 가 아닌 여러곳에서 참조될 수 있기 때문이다.