DECORATOR
DECORATOR
PROXY 에 해당되며 부가기능을 추가 하는 것이 목적이다. Proxy 패턴은 원본 클래스와 관련이 없는 기능을 추가하는 반면, Decorator 패턴은 Decorator 클래스가 원본 클래스와 관련이 깊은 기능을 추가한다.

Design Principles
- Open-Close Principle : 클래스는 확장에 대해서는 열려 있어야 하지만, 코드 변경에 대해서는 닫혀 있어야 한다.
- e.g 옵저버 패턴에서 옵저버를 새로 추가하면 Subject 자체에 코드를 추가하지 않아도 된다.
- 데코레이터 패턴은 객체 작성이라는 형식으로 실행중에 클래스를 꾸미는 방법 이다. 객체에 추가 요소를 동적으로 더할 수 있고, 서브클래스를 만드는 경우 상속에 비해 훨씬 유연하게 확장이 가능하다. 데코레이터 패턴을 사용하는 경우는 기존 코드는 건드리지 않은 채로 확장을 통해서 새로운 행동을 추가하고 싶은 경우 에 사용하면 된다. 데코레이터 패턴은 상속을 이용해서 형식을 맞춘다. 행동을 물려받는게 목적이 아님. 만약, 상속을 통해 행동을 물려받게 되면 서브클래스에서 오버라이딩한 메서드만 쓰기 때문에 안좋다. 따라서 구성(인스턴스 변수로 다른 객체를 저장, Composition) 을 이용해서 유연성을 확보한다.
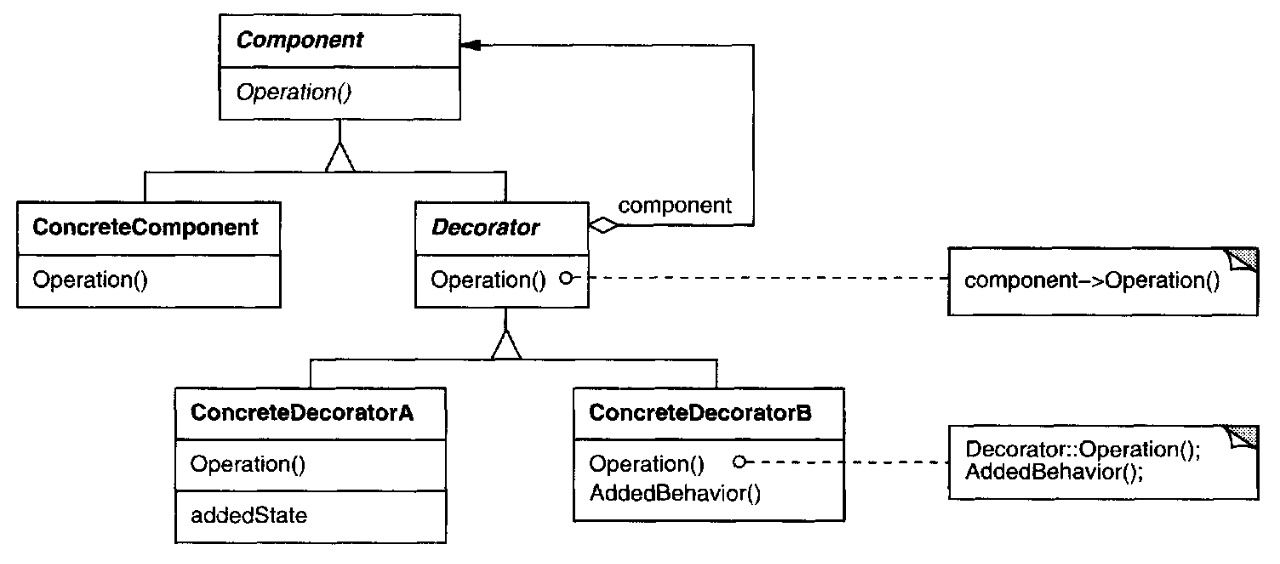
Decorator 구현체에 중복되는 기능들이 있을 수 있다. 이러한 기능들을 Decorator 라는 추상 클래스로 만들어 중복을 제거할 수 있는데, Decorator 추상 클래스 내부에서 Component 를 속성으로 가지고 있어야 한다. 이렇게 하면 추가로 클래스 다이어그램에서 어떤 것이 실제 컴포넌트 인지, 데코레이터인지 명확하게 구분할 수 있다. 이것이 바로 GOF 에서 설명하는 데코레이터 패턴이다.
The main components of the decorator pattern are:
- Component: An interface or abstract class that defines the common behavior of the objects that will be decorated. This component can also be a concrete class in some cases.
- Concrete Component: A concrete implementation of the component interface or class. This is the base object that will be decorated with new functionality.
- Decorator: An abstract class or interface that extends or implements the component interface. The decorator class maintains a reference to a component object and delegates the core behavior to that object. Decorators can add or override behavior as needed.
- Concrete Decorator: A concrete implementation of the decorator class that defines the specific additional functionality or behavior to be added to the component.
Java I/O Library

Java I/O Library 의 설계 사상을 분석해보자. InputStream, OutputStream 하위에 BufferedXXXStream 이 존재한다. BufferedInputStream 은 InputStream 을 확장하여 입력 데이터를 버퍼에 저장한 후, 필요할 때 버퍼에서 읽어오는 방식으로 동작한다. 이렇게 하면 매번 물리적인 I/O(read() 호출)를 수행하는 대신, 메모리에서 데이터를 읽는 방식으로 속도를 향상시킬 수 있다. 따라서 디스크 I/O 호출을 최소화할 수 있다.
이것을 사용하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(...);
InputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte[] data = new byte[128];
while (bin.read(data) != -1) {
...
}
Inheritance Based Design
Java I/O Library 가 상속(inheritance) 기반으로 설계되었다면, 다양한 InputStream 구현체 마다 새로운 버퍼링 클래스를 만들어 줘야 할 것이다.
class BufferedFileInputStream extends FileInputStream { /* 버퍼링 로직 추가 */ }
class BufferedByteArrayInputStream extends ByteArrayInputStream { /* 버퍼링 로직 추가 */ }
class BufferedPipedInputStream extends PipedInputStream { /* 버퍼링 로직 추가 */ }
이러한 설계의 문제는 클래스 개수가 기하급수적으로 증가하여 유지보수가 어려워진다는 것이다.
Decorator Pattern Based Design
데코레이터 패턴을 사용하면, 하나의 BufferedInputStream 을 만들고, 어떤 InputStream 이든 감싸서 사용하면 된다.
InputStream fileStream = new FileInputStream("example.txt");
InputStream bufferedStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileStream);
- 파일 스트림뿐만 아니라, 모든 InputStream 에서 버퍼링을 활용할 수 있음
- 새로운 스트림이 추가되더라도 BufferedInputStream 을 그대로 재사용 가능함
Decorator Class 는 원본 클래스와 동일한 상위 클래스를 상속 하기 때문에, 원본 클래스 내에 여러 개의 Decorator Class 를 중첩할 수 있다.
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("example.txt")));
이러한 설계는 새로운 기능(버퍼링)을 추가하면서도 기존 코드(InputStream 구현체들)를 수정할 필요가 없기 때문에 (기존 코드(FileInputStream 등)는 그대로 두고, 기능 확장만 가능) Open-Close Principle 을 준수한다.
Decorator 패턴은 Inheritance 와 Composition 을 적절히 사용한 패턴이다.
public class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {
protected volatile InputStream in; // Composition: 내부적으로 InputStream 을 포함
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in; // 외부 InputStream 을 감싼다 (데코레이터 패턴)
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read(); // 포함된 InputStream 의 read() 호출 (기본 동작)
}
}
- InputStream 은 추상 클래스(원본 클래스)이다. FilterInputStream 은 이러한 원본 클래스를 상속한다.
- FilterInputStream 은 기본적으로 내부적으로 포함된 InputStream 의 동작을 그대로 전달하는 역할을 한다.
- 하지만 하위 클래스에서 read()를 재정의하여 추가적인 기능(버퍼링, 암호화 등)을 구현할 수 있도록 설계되었다.
public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
protected volatile byte buf[]; // 데이터를 저장할 버퍼 배열
protected int count; // 버퍼 내 데이터 개수
protected int pos; // 현재 읽을 위치
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
this(in, 8192); // 기본 버퍼 크기 8KB
}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
buf = new byte[size];
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) { // 버퍼가 비었으면 다시 채우기
fill();
if (pos >= count) return -1; // EOF 처리
}
return buf[pos++] & 0xff; // 버퍼에서 읽기
}
private void fill() throws IOException {
count = in.read(buf, 0, buf.length); // 포함된 InputStream 에서 데이터 읽기
pos = 0;
}
}
만약 BufferedInputStream 이 원본 클래스인 InputStream 을 직접 상속한다면 중첩해서 사용하는 것이 불가능하다.
InputStream input = new FileInputStream("data.txt");
InputStream buffered = new BufferedInputStream(input);
InputStream data = new DataInputStream(buffered); // 불가능!
References
- Gangs of Four Design Patterns
- 设计模式之美 / 王争