FLYWEIGHT
designpattern
FLYWEIGHT
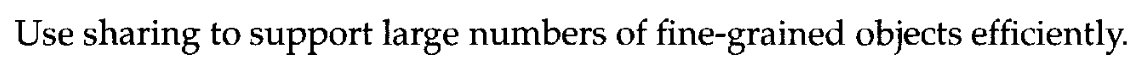
A flyweight is a shared object that can be used in multiple contexts simultaneously.
Flyweight 패턴은 객체를 재사용하여 메모리를 절약하는 것이다. 이때 공유되는 객체는 Immutable Object 여야 한다. 여기서 불변 객체는 객체가 생성자를 통해 성공적으로 생성된 후 객체가 포함하고 있는 변수 등의 값이나 상태가 변경되지 않는다는 것을 의미한다.
- 자주 변하는 속성(또는 외적인 속성, extrinsit)과 변하지 않는 속성(또는 내적인 속성, intrinsit)을 분리하고 재사용하여 메모리 사용을 줄일 수 있다.
- 자주 변하지 않는 속성을 Factory 로 객체를 생성하여 재사용할 수있다.
시스템에 많은 수의 불변 객체가 있다면, Flyweight 패턴을 사용할 수 있다.
Design Principles
Chess
// 체스 말의 종류를 정의하는 열거형
enum class ChessPieceType {
KING, QUEEN, ROOK, BISHOP, KNIGHT, PAWN
}
// 체스 말의 색상을 정의하는 열거형
enum class ChessPieceColor {
BLACK, RED
}
// 체스 말의 위치를 정의하는 클래스
data class Position(val x: Int, val y: Int)
// 플라이웨이트 인터페이스 - 체스 말
interface ChessPiece {
fun getType(): ChessPieceType
fun getColor(): ChessPieceColor
fun display(position: Position) // 외부 상태(position)를 매개변수로 받음
}
// 구체적 플라이웨이트 - 실제 체스 말 구현
class ConcretePiece(
private val type: ChessPieceType,
private val color: ChessPieceColor
) : ChessPiece {
override fun getType(): ChessPieceType = type
override fun getColor(): ChessPieceColor = color
override fun display(position: Position) {
// 실제 구현에서는 체스 말을 화면에 표시하는 로직이 들어갈 것
println("${color} ${type} at position (${position.x}, ${position.y})")
}
}
// 플라이웨이트 팩토리 - 체스 말 객체 생성 및 공유 관리
class ChessPieceFactory {
private val pieces = mutableMapOf<String, ChessPiece>()
fun getChessPiece(type: ChessPieceType, color: ChessPieceColor): ChessPiece {
// 키 생성: 타입과 색상을 조합
val key = "${type}_${color}"
// 기존 객체가 없으면 새로 생성
if (!pieces.containsKey(key)) {
pieces[key] = ConcretePiece(type, color)
println("Creating new chess piece: $key")
} else {
println("Reusing existing chess piece: $key")
}
return pieces[key]!!
}
fun getPieceCount(): Int = pieces.size
}
// 체스판 - 클라이언트 역할
class ChessBoard(private val id: Int, private val factory: ChessPieceFactory) {
// 체스판에 배치된 말들의 정보를 저장 (말의 참조와 위치)
private val piecesWithPositions = mutableMapOf<Position, ChessPiece>()
// 체스판 초기화
fun initialize() {
// 폰 배치
for (i in 0..7) {
addPiece(ChessPieceType.PAWN, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(i, 1))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.PAWN, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(i, 6))
}
// 룩 배치
addPiece(ChessPieceType.ROOK, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(0, 0))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.ROOK, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(7, 0))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.ROOK, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(0, 7))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.ROOK, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(7, 7))
// 나이트 배치
addPiece(ChessPieceType.KNIGHT, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(1, 0))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.KNIGHT, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(6, 0))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.KNIGHT, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(1, 7))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.KNIGHT, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(6, 7))
// 비숍 배치
addPiece(ChessPieceType.BISHOP, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(2, 0))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.BISHOP, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(5, 0))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.BISHOP, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(2, 7))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.BISHOP, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(5, 7))
// 퀸 배치
addPiece(ChessPieceType.QUEEN, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(3, 0))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.QUEEN, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(3, 7))
// 킹 배치
addPiece(ChessPieceType.KING, ChessPieceColor.BLACK, Position(4, 0))
addPiece(ChessPieceType.KING, ChessPieceColor.RED, Position(4, 7))
}
private fun addPiece(type: ChessPieceType, color: ChessPieceColor, position: Position) {
// 팩토리로부터 공유된 체스 말 객체를 가져옴
val piece = factory.getChessPiece(type, color)
// 위치 정보(외부 상태)와 함께 체스 말을 저장
piecesWithPositions[position] = piece
}
fun display() {
println("Displaying chess board #$id")
for (entry in piecesWithPositions) {
val position = entry.key
val piece = entry.value
piece.display(position)
}
println("----------------------------")
}
fun movePiece(from: Position, to: Position) {
if (piecesWithPositions.containsKey(from)) {
val piece = piecesWithPositions[from]!!
piecesWithPositions.remove(from)
piecesWithPositions[to] = piece
println("Moved piece from (${from.x}, ${from.y}) to (${to.x}, ${to.y})")
} else {
println("No piece at position (${from.x}, ${from.y})")
}
}
}
// 대기실 - 다수의 체스 방(체스판) 관리
class ChessLobby {
private val factory = ChessPieceFactory()
private val boards = mutableMapOf<Int, ChessBoard>()
fun createBoard(id: Int): ChessBoard {
val board = ChessBoard(id, factory)
board.initialize()
boards[id] = board
return board
}
fun getBoardCount(): Int = boards.size
fun getPieceInstanceCount(): Int = factory.getPieceCount()
}
// 메인 함수 - 플라이웨이트 패턴 테스트
fun main() {
val lobby = ChessLobby()
// 1000개의 체스판 생성
for (i in 1..1000) {
lobby.createBoard(i)
}
println("Total chess boards created: ${lobby.getBoardCount()}")
println("Total chess piece objects in memory: ${lobby.getPieceInstanceCount()}")
// 임의의 체스판에서 말 이동 테스트
val board = lobby.createBoard(1001)
board.display()
board.movePiece(Position(4, 0), Position(4, 1))
board.display()
}
- ChessPiece 인터페이스는 플라이웨이트 역할을 합니다. 내부 상태(말의 종류, 색상)와 외부 상태(위치)를 구분
- ConcretePiece 클래스는 실제 체스 말을 구현하여 내부 상태(말 종류, 색상)만 저장
- ChessPieceFactory 는 플라이웨이트 팩토리로, 체스 말 객체를 생성하고 공유합니다. 동일한 종류와 색상의 말이 요청되면 기존 객체를 재사용
- ChessBoard 클래스는 클라이언트 역할로, 체스 말의 위치(외부 상태)를 관리
-
ChessLobby 는 여러 체스판을 관리하는 클래스
- 이 구현의 핵심 이점은 체스 말의 실제 객체 수를 최소화하는 것이다. 예를 들어 1000개의 체스판을 생성해도 메모리에는 12개(6종류 × 2색상)의 체스 말 객체만 존재한다. 위치 정보는 각 체스판에서 외부 상태로 관리되어 메모리 사용량을 크게 줄인다.
Java; Integer.valueOf
- Integer.valueOf(int)
Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(10);
Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(10);
boolean result = i1 == i2;
result 는 true 가 나온다. 왜냐하면 내부적으로 자주 사용되는 값은 캐싱해두어서 같은 객체로 반환하기 때문이다.
Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(10000);
Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(10000);
boolean result = i1 == i2;
result 는 false 가 나온다. 자주 사용되는 값이 아니라서 서로 다른 객체가 반환된다.
원래 객체 비교하던 것 처럼 equals() 를 사용하여 비교하는게 낫다.
References
- Gangs of Four Design Patterns
- 设计模式之美 / 王争