PROXY
PROXY
Provide a surrogate for another object to control access to it.
Design Principles
Proxy 패턴은 특정 객체에 대한 접근을 제어하거나 기능을 추가 할 수 있는 패턴을 의미한다. 원본 클래스를 변경하지 않은 상태로 proxy class 를 도입하여 원본 클래스와 관련 없는 새로운 기능을 추가하는 것이다.
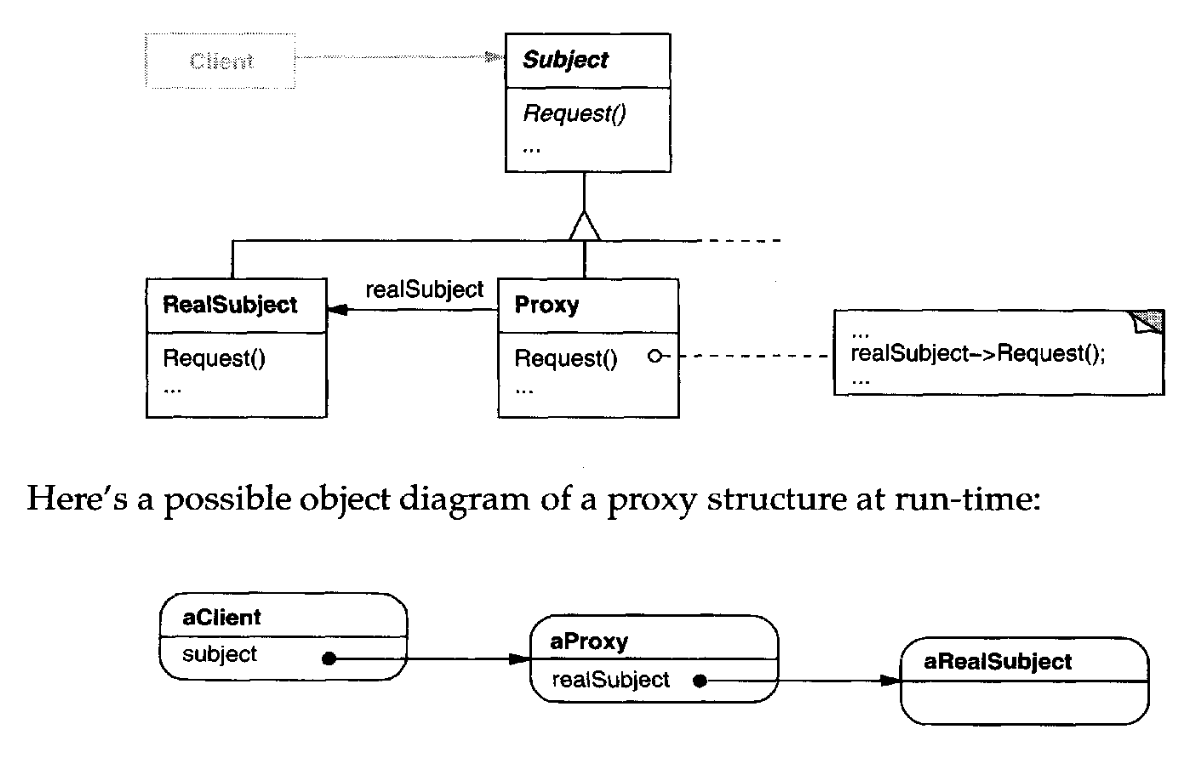
- Subject: This is the interface or abstract class that defines the operations that the real object and the proxy must implement.
- RealSubject: This is the real object that the proxy represents. It implements the operations defined in the subject interface.
- Proxy: This is the object that acts as a surrogate or placeholder for the real object. It implements the subject interface and delegates the operations to the real object.
Subject:
interface Subject {
fun doSomething(): Void
}
Real Subject:
class RealSubject: Subject {
override fun doSomething() {
// doSomething
}
}
Proxy class:
class Proxy: Subject {
private val realSubject = RealSubject()
override fun doSomething(): Void {
// doSomething (caching, logging ...
return realSubject.doSomething() // delegation
}
}
Remote Proxy
GoF 디자인 패턴에서는 RPC 에서 프록시 패턴을 적용하는 것을 Remote Proxy 로 정의하고 있다.
원격 프록시(Remote Proxy)는 프록시는 로컬에 있고, RealSubject 가 원격 서버(다른 서버)에 존재하는 경우 사용할 수 있다. 프록시는 네트워크 통신을 통해 클라이언트 요청을 RealSubject 로 전달한다.
Subjects:
interface ProductService {
fun getProducts(): List<Product>
}
Next, we define the real subject class that implements the ProductService interface and fetches the list of products over the network:
class RemoteProductService : ProductService {
override fun getProducts(): List<Product> {
// Fetch products over the network
Thread.sleep(5000) // Simulate network delay
return listOf(Product("Product 1"), Product("Product 2"), Product("Product 3"))
}
}
data class Product(val name: String)
Now, we define the remote proxy class that implements the ProductService interface and delegates the operations to the real subject class:
class RemoteProductServiceProxy : ProductService {
private val realService = RemoteProductService()
override fun getProducts(): List<Product> {
// Check if the list of products is already cached
// If yes, return the cached list
// Otherwise, fetch the list from the remote service
return realService.getProducts()
}
}
Finally, we can use the remote proxy to fetch the list of products without incurring the overhead of network communication:
fun main() {
val productService: ProductService = RemoteProductServiceProxy()
// Fetch the list of products
val products = productService.getProducts()
// Print the list of products
println("Products:")
products.forEach { println(it.name) }
}
클라이언트는 서버와의 상호 작용에 대한 세부 사항은 알지 못한 채 RPC 서비스를 기본 기능인 것처럼 사용할 수 있다.
Virtual Proxy
객체 생성 작업이 무거울때 사용하는 Lazy Initialization 방식
First, we define the subject interface that defines the operations for loading and displaying the image:
interface Image {
fun display()
}
Next, we define the real subject class that implements the Image interface and loads the actual image:
class RealImage(private val filename: String) : Image {
init {
loadFromDisk()
}
private fun loadFromDisk() {
// Load the image from the disk
println("Loading image from disk: $filename")
}
override fun display() {
// Display the image
println("Displaying image: $filename")
}
}
Now, we define the virtual proxy class that implements the Image interface and creates the real subject object only when it is needed:
class VirtualImage(private val filename: String) : Image {
private var realImage: RealImage? = null
override fun display() {
// Create the real image object only when it is needed
if (realImage == null) {
realImage = RealImage(filename)
}
// Display the image
realImage?.display()
}
}
Protection Proxy
보호 프록시의 목적은 접근 권한을 제어하는 것이다.
First, we define the subject interface that defines the operations for accessing the information:
interface InformationService {
fun getInformation(): String
}
Next, we define the real subject class that implements the InformationService interface and provides access to the sensitive information:
class RealInformationService : InformationService {
override fun getInformation(): String {
return "Sensitive information"
}
}
Now, we define the protection proxy class that implements the InformationService interface and checks the permissions before granting access to the sensitive information:
class ProtectionInformationService(private val informationService: InformationService, private val user: String) : InformationService {
override fun getInformation(): String {
// Check if the user has the proper permissions
if (user == "admin") {
// Grant access to the sensitive information
return informationService.getInformation()
} else {
// Deny access to the sensitive information
throw SecurityException("Access denied")
}
}
}
Finally, we can use the protection proxy to restrict access to the sensitive information:
fun main() {
// Create the real subject object
val realService: InformationService = RealInformationService()
// Create a protection proxy for the information service
val informationService: InformationService = ProtectionInformationService(realService, "admin")
// Get the sensitive information
val information = informationService.getInformation()
// Print the sensitive information
println("Information: $information")
}
Dynamic Proxy
프록시 패턴의 단점은, 원본 클래스에 대한 프록시 클래스를 생성해야한다. 이 개수가 많아진다면 프로젝트의 클래스 수가 증가하고 코드의 유지 관리 비용이 증가한다. 또한 프록시 클래스의 코드는 원본 코드와 유사하므로 불필요한 개발 리소스도 들어간다는 단점이 있다.
이를 위해서 Reflection 기반의 Dynamic Proxy 를 활용할 수 있다.
Aspect Oriented Programming(AOP) 의 주요 패러다임 중 하나가 트랜잭션 관리, 로깅, 유효성 검사 등과 같은 관심사를 분리하는 것이다. 따라서 AOP 를 많이 사용하는 프레임워크가 Proxy Mechanism 에 의존하는 것은 당연하다.
References
- Gangs of Four Design Patterns
- 设计模式之美 / 王争