Functions
Currying, Partial Application
Functions
Functions that input or output functions or take functions as parameters are called high-order functions, often abbreviated to HOFs.
Backgrounds
Three characteristics of Functional Programming:
- Higher Order Functions
- Pure Functions
- Immutable Data
Components of Code in Functional Programming
- Action
- Calculate
- Data
Differences From Object Oriented Programming
For example, say that we have a large program that is assembled from smaller pieces.
- In oop approach, these pieces would be class and objects.
- In fp approach, these pieces would be functions.
Or say that we need to parameterize some aspect of the program, or we want to reduce coupling between components.
- In oop approach, we would use interfaces and dependency injection.
- In fp approach, we would parameterize with functions.
Or let's say that we want to follow the "Don't repeat yourself" principle and reuse code between many components.
- In oop approach, we might use inheritance or technique like the Decorator Pattern.
- In fp approach, we put all the reusable code into functions and glue them together using components.
Go 에서는 Method 와 Function 을 사용할 수 있는데, Difference Between Method And Function 를 읽어보면 좋다.
Currying
Any multi-parameter function can be converted into a series of one-parameter functions. This method is called currying.

Examples:
// 두 개의 인자를 받는 일반적인 함수
fun add(x: Int, y: Int): Int {
return x + y
}
// Currying - 커링을 적용한 함수
fun curriedAdd(x: Int): (Int) -> Int {
return { y: Int -> x + y }
}
// 사용 예제
fun main() {
// 일반 함수 사용
val result1 = add(2, 3)
println("add(2, 3) = $result1") // Output: add(2, 3) = 5
// 커링이 적용된 함수 사용
val addTwo = curriedAdd(2)
val result2 = addTwo(3)
println("curriedAdd(2)(3) = $result2") // Output: curriedAdd(2)(3) = 5
// 한 줄로도 사용할 수 있음
val result3 = curriedAdd(2)(3)
println("curriedAdd(2)(3) = $result3") // Output: curriedAdd(2)(3) = 5
}
Partial Application
Partial Application says "if you fix the first arguments of the function, you get a function of the remaining arguments".
For example, the 'sayGreeting' function below has two parameters:
// sayGreeting: string -> string -> unit
let sayGreeting greeting name =
printfn "%s %s" greeting name
But we can pass in just one parameter to create some new functions with the greeting baked in:
// sayHello: string -> unit
let sayHello = sayGreeting "Hello"
// sayGoodbye: string -> unit
let sayGoodbye = sayGreeting "Goodbye"
These functions now have one remaining parameter, the name. If we supply that, we get the final ouput:
sayHello "Alex"
// output: "Hello Alex"
sayGoodbye: "Alex
// output: "Goodbye Alex"
This approach of "baking in" parameters is called partial application and is a very important functional pattern.
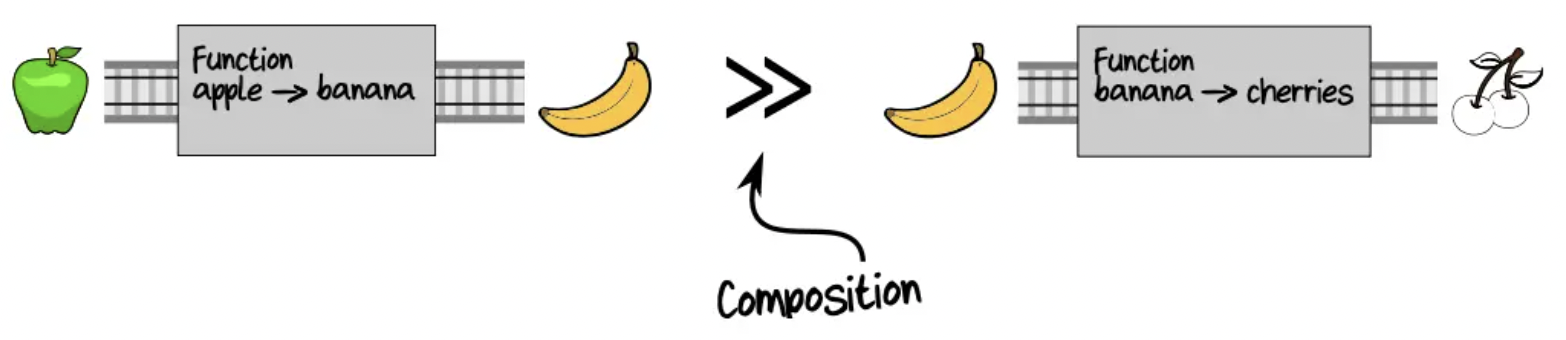
Composition
Function composition 이란 information hiding 의 기능을 가지고 있다.
아래 예제에서, 사과를 통해 체리를 만들기 위해서는 2개의 Pipeline 이 연결되어야 하고, 이때 중간값인 바나나에 대해서 알고 있어야 한다. 하지만, 함수를 사용하는 입장에서 중간값은 관심사(aspect) 가 아니다. 따라서 함수 합성을 통해서 관심사가 아닌 부분을 숨길 수 있다.
Composition of functions as piping:
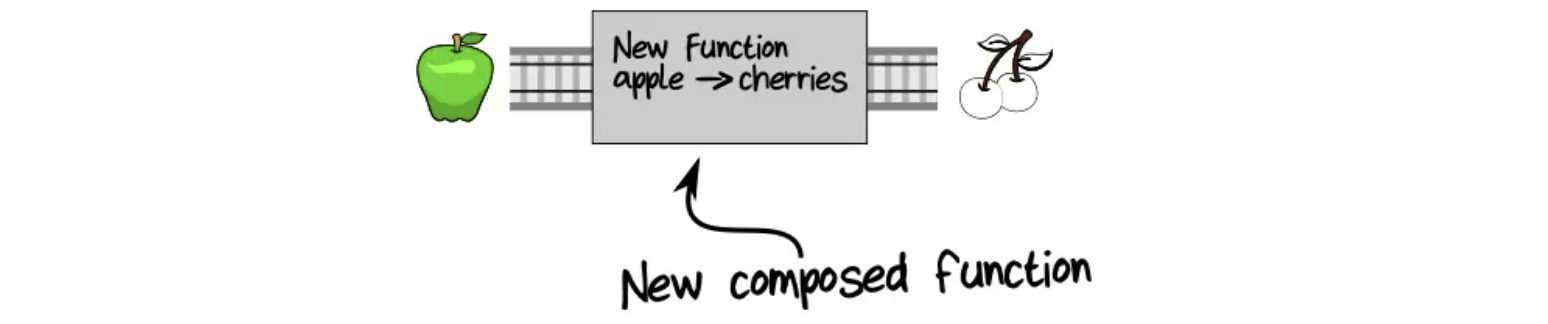
The result of the composition is a new function:
Code:
let isEven x = // int -> bool function
(x % 2) = 0
let printBool x = // bool -> string function
sprintf "value is %b" x
let isEventThenPrint x =
x |> isEven |> printBool
Asking Questions
함수형 프로그래밍을 사용하는 경우 "How do I implement the Strategy Pattern ?" 보다 "How can I parameterize behavior ?" 와 같은 질문을 던지는 것이 좋다.
Links
References
- Domain Modeling Made Functional / Scott Wlaschin / The Pragmatic Programmers