Pointers and Dereferencing
go
Pointers
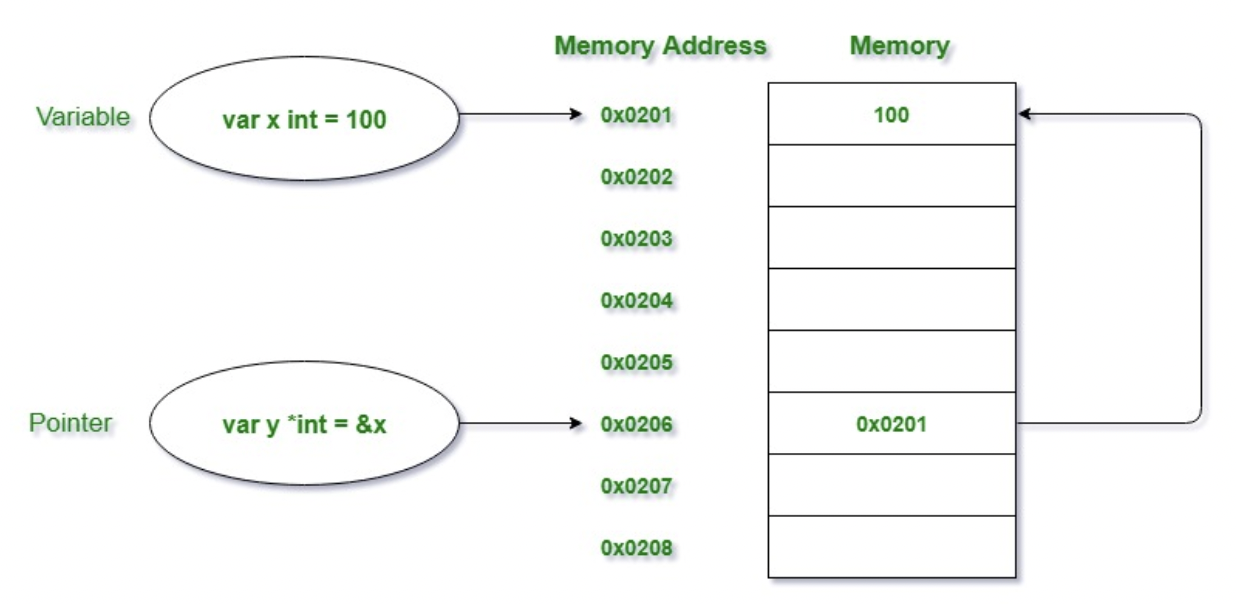
Pointers reference a location in memory where a value is stored rather than the value itself. By using a pointer (*int), the zero function is able to modify the original vari‐ able.
- Go a pointer is represented using the
*(asterisk) character followed by the type of the stored value *(dereferencing operator)is also used to “dereference” pointer variables. Dereferencing a pointer gives us access to the value the pointer points to.&(address operator)operator to find the address of a variable.
Dereferencing
func zero(xPtr *int) {
*xPtr = 0
}
func main() {
x := 5
zero(&x)
fmt.Println(x) // x is 0
}
*xPtr = 0 과 같이 데이터를 쓰기 위해서는 * 를 사용하여 포인터를 사용 해야 한다. 이것을 역참조(Dereferencing) 이라고 한다.
new
new 키워드를 통해서 포인터를 얻을 수 있다.
func one(xPtr *int) {
*xPtr = 1
}
func main() {
xPtr := new(int)
one(xPtr)
fmt.Println(*xPtr) // x is 1
}
Why use pointers in Go?
Pointers in Golang 에 왜 포인터를 사용해야하는지 자세히 나와있다.

Declaration and Initialization of Pointers: