Continuation Passing Style
Continuation Passing Style
Debugging to analyze suspend mechanisms 에서 코루틴들이 중단-재개 되면서 함수 내에 사용되는 지역변수 정보들을 컨티뉴에이션에 저장하고 가져다 사용하는 것을 확인했다. Continuation 의 경우 실제 Function 에서 Thread Stack 영역에 물고 있어야 하는 정보를 저장하는 역할을 담당한다.
CPS(Continuation Passing Style) 변환은 프로그램의 실행 중 특정 시점 이후에 진행해야 하는 내용을 별도의 함수로 뽑고(이런 함수를 Continuation 이라 함), 그 함수에게 현재 시점까지 실행한 결과를 넘겨서 처리하게 만드는 소스코드 변환 기술이다.
KotlinConf 2017 - Deep Dive into Coroutines on JVM by Roman Elizarov 영상 내용이 CPS 를 이해하기에 좋다.
A toy problem:
fun postItem(item: Item) {
val token = requestToken()
val post = createPost(token, item)
processPost(post)
}
위 세 연산은 코루틴으로 만들어 처리하면 Continuation Passing Style 이 적용되어 아래와 같이 컴파일 된다.
fun postItem(item: Item) {
requestToken { token ->
// Continuations
val post = createPost(token, item)
processPost(post)
}
}
callback 과 상당히 유사하다. 영상에서는 다음과 같이 표현하고 있다.
- CPS is fancy theoretical name of callback
- CPS == Callback
compile suspend function:
suspend fun createPost(token: Token, item: Item): Post { ... }
위 코드가 컴파일되면 아래와 같이 변한다.
// Java/JVM
Object createPost(Token token, Item item, Continuation<Post> cont) { ... }
suspend 키워드가 사라지고 Continuation 이 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이것을 CPS 라고 한다.

Continuation is generic callback interface
Labeling
suspend function 은 중단될 수 있는 함수이다. 중단이 되었다가 다시 시작하려면 현재 실행중이 었던 위치를 기록해뒀다가 재개 될 때 다시 시작 되어야 한다.
위에서 작성했던 함수들이 suspend 함수라면 중단될 수 있는 포인트마다 내부적으로 Labeling 을 하게 된다.
suspend fun postItem(item: Item) { // suspend function
switch (label) {
case 0:
val token = requestToken() // suspend function
case 1:
val post = createPost(token, item) // suspend function
case 2:
processPost(post) // suspend function
}
}
Labeling 이 끝나면 Continuation Passing Style 을 적용하여 아래와 같이 컴파일 된다. switch 문으로 변경된다.
fun postItem(item: Item, cont: Continuation) {
val sm = object : CoroutineImpl { … }
switch (sm.label) {
case 0:
val token = requestToken(sm)
case 1:
val post = createPost(token, item, sm)
case 2:
processPost(post)
}
}
각 단계가 종료될때 postItem 을 다시 호출해서 재개(resume) 시켜야 한다. 그러기 위해서는 Continuation 을 인자로 넘겨야 한다.
State Machine is Continuation
Continuation Passing Style with Labeling:
class PostItemService {
private abstract class PostItemContinuation(val item: Item): Continuation {
var label = 0
var token: Token? = null
var post: Post? = null
}
// Last Argument is Continuation
fun postItem(item: Item, continuation: Continuation?) {
// Label 을 기준으로 상태를 관리한다.
// sm: State Machine
val sm = continuation as? PostItemContinuation ?: object : PostItemContinuation(item) { // State Machine is Continuation
override suspend fun resumeWith(data: Any?) {
when (super.label) {
0 -> { // label 이 0 인 경우 requestToken 이 호출되었음을 알 수 있다.
label = 1
token = data as Token
}
1 -> { // label 이 1 인 경우 createPost 가 호출되었음을 알 수 있다.
label = 2
post = data as Post
}
}
// Recursive Call
postItem(item, this) // Continuation Passing Style
}
}
when (sm.label) {
0 -> {
requestToken(sm) // Continuation Passing Style
}
1 -> {
createPost(sm.token!!, item, sm) // Continuation Passing Style
}
}
// when clause 가 종료되었다는 것은 마지막 라벨 상태인 것이다.
processPost(sm.post!!, sm) // Continuation Passing Style
}
}
위 처럼 구현하게 되면, Continuation 을 통해 최초 호출인지 아닌지 구분이 가능하며, PostItemContinuation 구현체에서 label 과 data 를 관리할 수 있다. 즉, Continuation 의 resumeWith 에서 label 을 증가시키고 data 를 적재하는 작업을 한다.
다른 suspend function 은 아래 처럼 구성이 된다.
suspend fun requestToken(continuation: Continuation) {
// do something
delay(100L)
// continuation.resumeWith 을 호출하면서 결과를 같이 넘겨준다.
continuation.resumeWith("requestToken result")
}
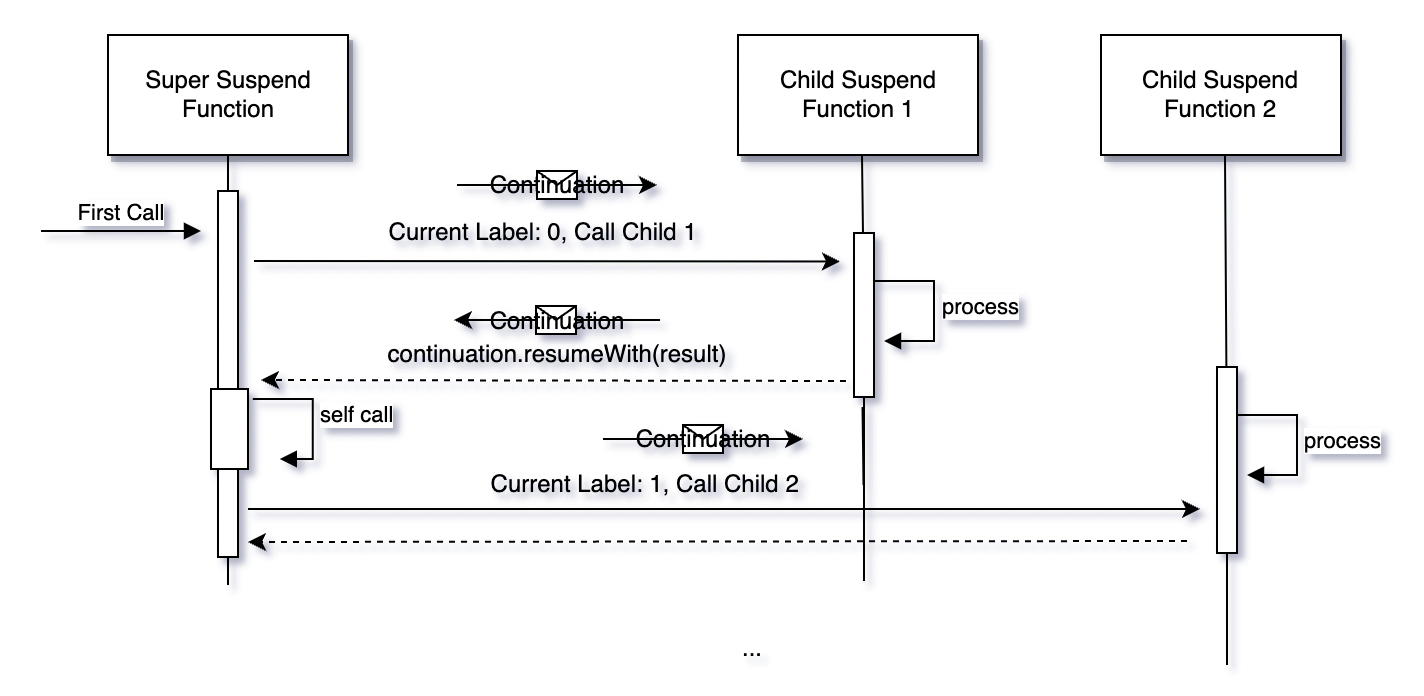
Flow:
Links
References
- 코틀린 완벽 가이드 / Aleksei Sedunov 저 / 길벗
- Kotlin In Action / Dmitry Jemerov, Svetlana Isakova 공저 / 에이콘