Message Delivery in Event Driven Architecture
Transactional Outbox, Polling Publisher, Message Broker
Transactional Outbox
How to reliably/atomically update the database and send messages/events?
Database 와 Event 를 같이 사용하고 있을 때, 어떻게 안전하고 원자적으로 Update 할 수 있을까?
Solution:
- A service that uses a relational database inserts messages/events into an outbox table (e.g. MESSAGE) as part of the local transaction. An service that uses a NoSQL database appends the messages/events to attribute of the record (e.g. document or item) being updated. A separate Message Relay process publishes the events inserted into database to a message broker.
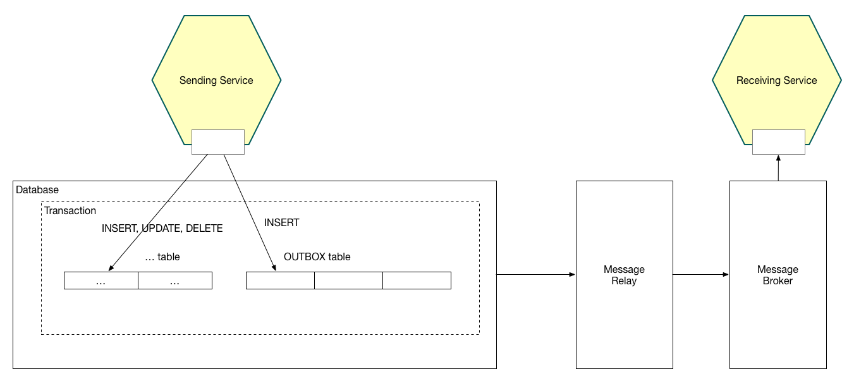
위 그림은 Transactional Outbox 패턴을 적용한 CDC(Change Data Capture) 예제이다.
The Eventuate CDC service works in one of two ways:
- Transaction log tailing - currently implemented for MySQL and Postgres WAL
- Polling
Outbox Table
Outbox table is often used as a message queue.
An outbox table can be implemented in a variety of ways, but is often used to store messages in a relational database, such as PostgreSQL or MySQL.
Field Types:
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| event_id(PK) | BIGINT | 이벤트의 순서를 보장할 수 있는 값을 가져야 함 |
| created_at | Datetime(3~6) | 이벤트 발생 시간(milliSec, nanoSec 등 정확도를 설정) |
| status | smallint | Ready(0) / Done(1) |
| payload | jsonb | JSON 타입의 Message Payload |
Transactional Outbox Sample Code:
@Service
public class CreateTaskService implements CreateTaskUserCase {
@Transactional
public CreateTaskResponse createTask(CreateTaskCommand createTaskCommand) {
taskRepository.save(task);
eventRepository.save(CreateTaskEvent.of(task));
}
}
Polling Publisher
Polling process checks the data source at regular intervals, typically by sending a request and waiting for a response, to determine if there are any new updates or changes.
Polling Publisher 는 데몬이나 스케줄러를 하나 띄워서 DB 에 저장된 이벤트를 주기적으로 Polling 하여 발행(publish) 하는 역할을 한다.
- Polling Publisher Sample code:
@Service
public class MessagePublisher {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * *")
@Transactional
public void publish() {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
eventRepository.findByCreateAtBefore(now, EventStatus.READY)
.stream()
.map(event -> restTemplate.execute(event))
.map(event -> event.done())
.forEach(eventRepository::save);
}
}
Benefits and Drawbacks
Transactional Outbox + Polling Publisher 는 실시간 처리가 필요한 곳에는 부적합함. 대용량 이벤트를 발행해야하며, 하나의 트랜잭션 안에서 많은 양의 이벤트가 생성된다면 Transactional Outbox 패턴은 부적합함.
Benefits:
- REST-API 환경에서 At-least-once 를 구현할 수 있음
Drawbacks:
- Polling, Publisher 과정에 의한 지연 처리
- DB 부하
- DB 에 비례한 처리 속도
Transaction Log Tailing
Tail the database transaction log and publish each message/event inserted into the outbox to the message broker.
The mechanism for trailing the transaction log depends on the database:
- MySQL binlog
- Postgres WAL
- AWS DynamoDB table streams
Message Broker
Kafka 와 같은 Message Broker 를 사용한다면 대용량 이벤트 처리를 할 수 있다.
Auto-commit 을 false 로 설정하고 Consumer Acknowledgement 을 구현하면 좋다.
In summary, if you are dealing with large amounts of events generated in a single transaction, using a message broker like Apache Kafka can be a better solution than using the Transactional Outbox pattern, as it provides more scalability, performance, and reliability for event processing.