Netty ByteBuf
reactive netty
ByteBuffer
Java NIO provides ByteBuffer as its byte container. Netty’s alternative to ByteBuffer is ByteBuf. ByteBuf is Netty’s data container.
ByteBuf
Characteristics:
- It’s extensible to user-defined buffer types.
- Transparent zero-copy is achieved by a built-in composite buffer type.
- Capacity is expanded on demand (as with the JDK StringBuilder).
- Switching between reader and writer modes dosen’t require calling ByteBuffer’s flip() method.
- Reading and writing employ distinct indices.
- Method chaining is supported.
- Reference counting is supported.
- Pooling is supported.
Random Access Indexing
ByteBuf uses zero-based indexing.
ByteBuf buffer = ...;
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i ++) {
byte b = buffer.getByte(i);
System.out.println((char) b);
}
Sequential Access Indexing
ByteBuf 는 readerIndex, writerIndex 를 가지고 있다. read/write index 는 각각 read/write operation 이 일어날 때마다 증가한다.
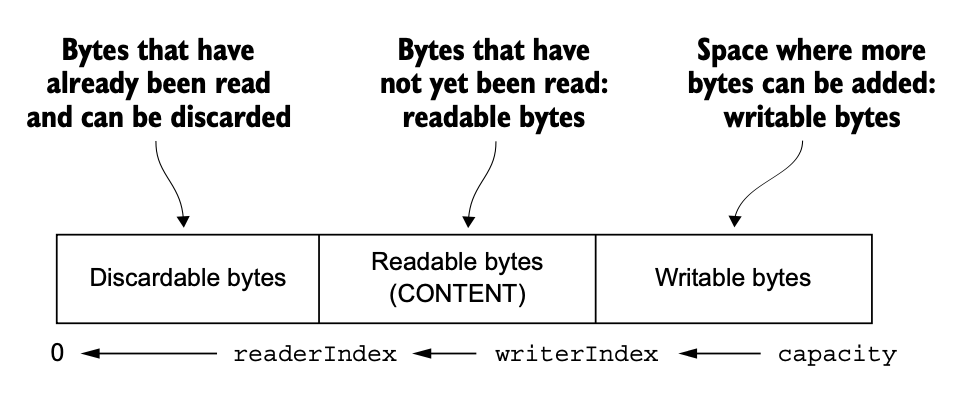
Read:
// Iterates the readable bytes of a buffer.
ByteBuf buffer = ...;
while (buffer.isReadable()) {
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
}
Write:
// Fills the writable bytes of a buffer with random integers.
ByteBuf buffer = ...;
while (buffer.maxWritableBytes() >= 4) {
buffer.writeInt(random.nextInt());
}
Conversion to existing JDK types
Netty ByteBuf Docs - Conversion to existing JDK types
Backing Array
The most frequently used ByteBuf pattern stores the data in the heap space of the JVM. Referred to as a backing array.
Reference Counting
ByteBuf 는 readerIndex, writerIndex 외에도 ReferenceCounted 를 구현하여 누가 얼마나 참고하고 있는지 refCnt 를 가지고 있다.
ReferenceCounted 는 retain() 과 release() 를 제공한다. retain 은 참조를 증가시키는 것이고, release 는 해제하는 것이다.
ReferenceCountUtil 를 사용하여 ReferenceCounted 를 다룰 수 있다.
ReferenceCountUtil.refCnt(data); // get refCnt
Links
Reference
- Netty In Action / Trustin Lee 저 / MANNING