Design to Performance; Redis Single-Threaded Architectures
Design to Performance; Redis Architecture
Redis(Remote dictionary server) 는 High Performance Key-Value Based In-memory NoSQL Database 이다.
Key-Value 형식의 NoSQL("Not Only SQL"의 약자로, SQL 기반의 데이터베이스가 아닌 다양한 데이터 모델을 지원한다는 의미)은 단순하기 때문에 빠르다. 그렇기 때문에 scale-out 이 쉽다. 즉, 단순한 구조로 인한 빠른 데이터 액세스와 처리 속도를 보장한다.
In-Memory 형태의 데이터베이스는 Disk 가 아닌 데이터가 Memory 에서 관리된다. 따라서, 장애 발생시 데이터가 휘발될 수 있다.
이제 부터가 중요하다. Redis 가 왜 Single Thread 로 설계되었고 고성능인지를 이해하기 위해서는 CS Level 로 깊게 들어가야 한다.
Suspend/Resume Mechanism
CPU 가 높은 처리량을 갖는 이유에 대해서 살펴보자. Designing Context Structures for Suspend/Resume in Multitasking; CPU 는 한 번에 한 가지 일만 할 수 있다. 하지만 우리는 여러 프로그램을 돌리는데 어떻게 동시에 동작하는 것 처럼 보이는 것일까?
그 이유는 ProgramA 에서 ProgramB 로 전환이 일어날 때 suspend/resume mechanism 으로 인해 전환 빈도(conversion frequency)가 빠르다는 점이다.
High Concurrency; Multiplexing
UNIX 세계에서 '모든 것은 파일이다' 라는 말이 있다. 사실상 모든 입출력 장치(드라이버, 키보드, 프린트 등)는 File 이라는 개념으로 ABSTRACTION 된다. 따라서 모든 입출력(I/O)는 파일 읽기(read)와 쓰기(write)로 구현할 수 있다.
Linux 에서는 파일 디스크립터(file descriptor) 라는 것을 이용한다. 파일 서술자는 번호에 불과하다. 예를 들어 유명한 식당에서 밥을 먹기위해 줄을 서는 경우, 종업원이 대기자들에게 대기 번호를 주는데 이 대기 번호가 파일 서술자이다.
char buffer[LEN];
int fd = open(file_name); // 파일 서술자 얻기
read(fd, buffer);
하나의 스레드에서 서버가 동시에 여러개의 사용자 요청을 처리하는 상황을 생각해보자.
if(read(socket_fd1, buff) > 0) {
// Do something
}
if(read(socket_fd2, buff) > 0) {
// Do something
}
일반적으로 read 함수는 Blocking 된다. 만약 첫 번째 사용자가 아무런 데이터를 보내지 않으면, 다음 코드를 실행할 없고 스레드가 일시중지될 것이다.
이를 해결하기 위한 방법으로 Multi-Thread 를 생각하겠지만 멀티 스레드는 C10K 문제를 해결하지 못한다. Multi-Thread 환경에서 스레드 수를 늘리는 것도 한계가 있고(memory 증가, context switching 문제 등) 결국, 많은 클라이언트 요청을 처리하기엔 확장성 문제가 발생한다는 것이다.
MultiPlex 라는 다중화 기법을 사용해야 하는데, 이는 파일 디스크립터 중에서 이벤트(데이터 준비, 연결 요청 등)가 발생하면 알려주는 매커니즘 이다. 이것을 입출력 다중화(I/O Multiplexing) 라고 한다. 하나의 스레드(또는 프로세스)가 여러 입출력 작업(I/O 작업)을 동시에 처리할 수 있도록 지원하는 기술이다. 이를 통해 많은 클라이언트와의 연결을 효율적으로 관리할 수 있다.
Understand Multiplexing
- Clerk(점원): Redis의 이벤트 루프. 단일 스레드로 모든 클라이언트 연결을 관리합니다.
- Clients(고객): Redis에 연결된 클라이언트(소켓 연결). 요청을 서버에 보냅니다.
- Order(주문): 클라이언트가 Redis에 요청하는 작업(명령어).
- Order List(주문 목록): Redis의 작업 대기열. 처리해야 할 명령어가 저장되는 큐입니다.
- Barista(바리스타): Redis의 쿼리 스레드. 작업(명령어)을 실행하는 역할을 합니다.
- Dynamically Hiring Baristas(바리스타 고용): Redis는 동적으로 쿼리 스레드를 생성하여 여러 작업을 병렬로 처리할 수 있습니다.
- Using the alarm system to wake itself up: Redis는 Linux의 select 또는 epoll을 사용해 소켓이 읽기/쓰기 준비 상태가 되면 이벤트 루프를 호출하여 작업을 처리합니다.
입출력 다중화(I/O Multiplexing) 와 같은 작동 방식 중 Linux 에서 가장 유명한 것이 epoll 이다.
// epoll 생성
epoll_fd = epoll_create();
// File Descriptor 를 epoll 이 처리하도록 지정
Epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, fd1, fd2, fd3, fd4, fd5, ...);
while(1) {
int n = epoll_wait(epoll_fd); // get event
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 이벤트 처리 - handler(event)
}
}
이렇게 이벤트가 도착할 때 까지 기다리다가, 이벤트가 도착하면 이벤트 처리 함수인 이벤트 핸들러를 찾아서 이벤트 핸들러를 호출하기만 하면 되는데 이러한 패턴을 reactor pattern 이라고 한다.
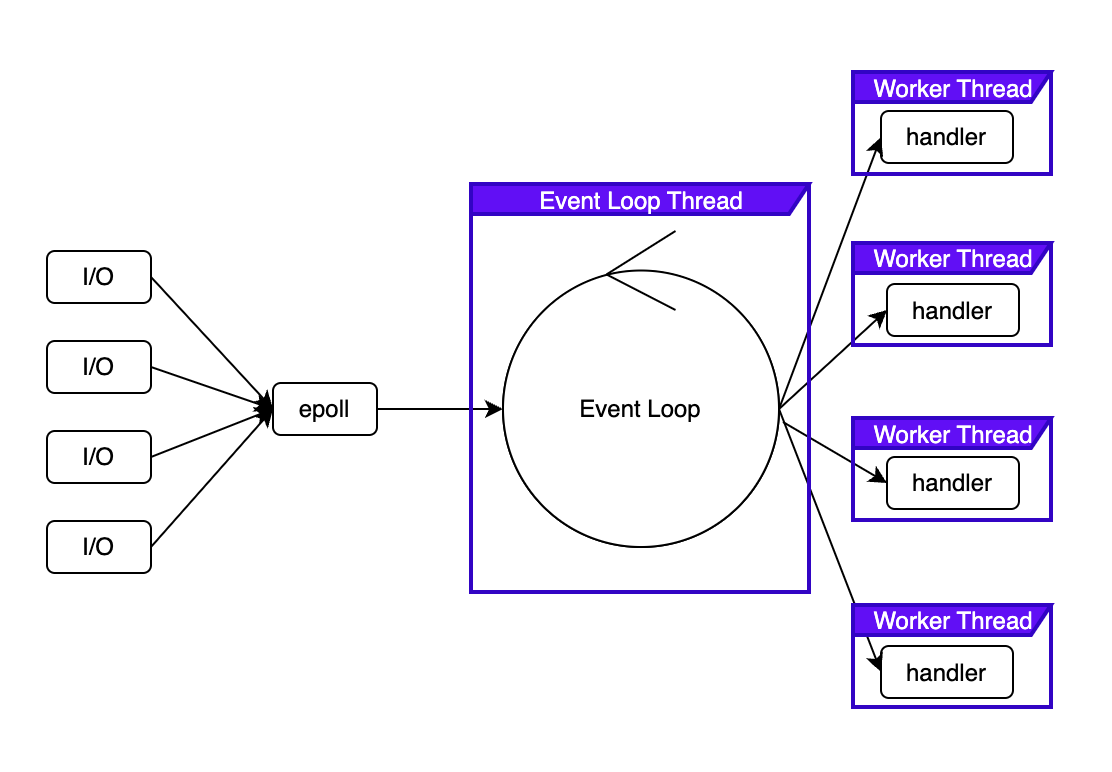
이러한 구조이기 때문에, Event Loop 내에서는 절대로 Blocking 인터페이스가 호출되면 안된다. 호출하는 순간 이벤트 순환 스레드가 일시 중지될 수 있고 이는 작업자 스레드 모두에게 영향을 준다. 따라서 Event Loop 내에서는 Non Blocking 작업만 진행되어야 한다.

Redis is single-threaded with epoll/kqueue and scale indefinitely in terms of I/O concurrency.
Redis 가 High Concurrency 를 위해서 Single Thread 기반의 아키텍처를 채택하였고, 내부적으로는 epoll, kqueue 와 같은 Multiplexing 기술을 사용한다는 것을 알 수 있다.
즉, 이벤트 루프 방식으로 동작하기 때문에 적은 수의 스레드로도 높은 동시성을 유지할 수 있으며, 작업이 Atomic 하기 때문에, 멀티스레드 애플리케이션에서 요구되는 동기화나 잠금 매커니즘 없이도 안정적이고 빠르게 사용자 요청을 처리할 수 있다.
Redis 는 싱글 스레드로 동작하기 때문에 오래 걸리는 작업(커맨드)을 수행하면 그 작업이 완료될 때 까지 대기해야 하므로 장애가 발생할 수 있다.
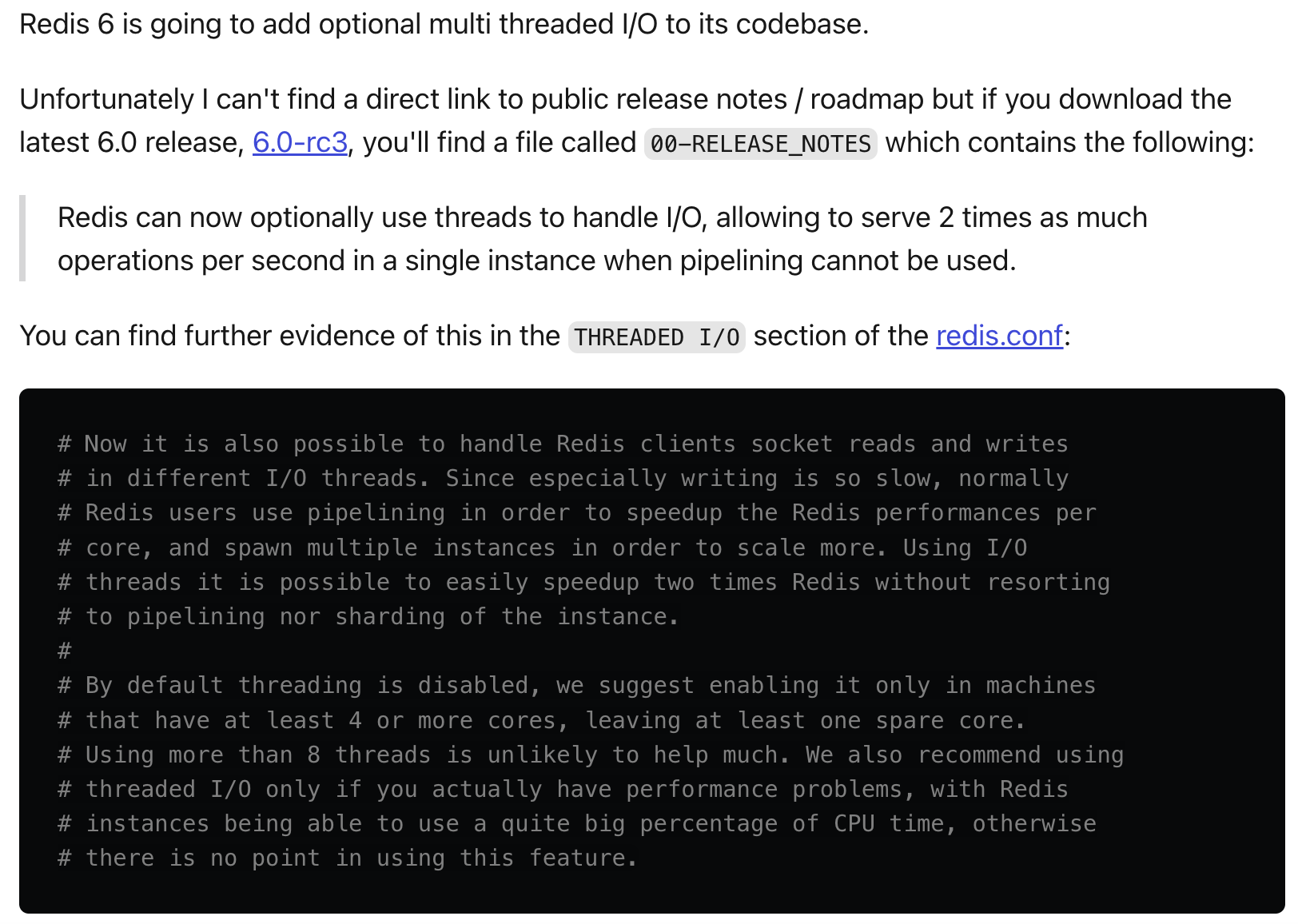
명령은 Single-Thread 로 처리하며, 선택적으로 스레드를 사용하여 I/O를 처리할 수 있다.
# Redis is mostly single threaded, however there are certain threaded
# operations such as UNLINK, slow I/O accesses and other things that are
# performed on side threads.
#
# Now it is also possible to handle Redis clients socket reads and writes
# in different I/O threads. Since especially writing is so slow, normally
# Redis users use pipelining in order to speed up the Redis performances per
# core, and spawn multiple instances in order to scale more. Using I/O
# threads it is possible to easily speedup two times Redis without resorting
# to pipelining nor sharding of the instance.
#
# By default threading is disabled, we suggest enabling it only in machines
# that have at least 4 or more cores, leaving at least one spare core.
# Using more than 8 threads is unlikely to help much. We also recommend using
# threaded I/O only if you actually have performance problems, with Redis
# instances being able to use a quite big percentage of CPU time, otherwise
# there is no point in using this feature.
#
# So for instance if you have a four cores boxes, try to use 2 or 3 I/O
# threads, if you have a 8 cores, try to use 6 threads. In order to
# enable I/O threads use the following configuration directive:
#
# io-threads 4
#
# Setting io-threads to 1 will just use the main thread as usual.
# When I/O threads are enabled, we only use threads for writes, that is
# to thread the write(2) syscall and transfer the client buffers to the
# socket. However it is also possible to enable threading of reads and
# protocol parsing using the following configuration directive, by setting
# it to yes:
#
# io-threads-do-reads no
#
# Usually threading reads doesn't help much.
#
# NOTE 1: This configuration directive cannot be changed at runtime via
# CONFIG SET. Also, this feature currently does not work when SSL is
# enabled.
#
# NOTE 2: If you want to test the Redis speedup using redis-benchmark, make
# sure you also run the benchmark itself in threaded mode, using the
# --threads option to match the number of Redis threads, otherwise you'll not
# be able to notice the improvements.
Links
- Single-threaded Event Loop Architecture for Building Asynchronous, Non-Blocking, Highly Concurrent Real-time Services
- redis.conf
References
- The secret of the underlying computer / lu xiaofeng
- REDIS FOR DEVELOPERS / 김가림 저 / 에이콘